订阅与广播
订阅
功能介绍
在流/批计算场景,上游业务系统会把数据发送至消息队列。但并不是按聚合根用户定义的命令的协议,而是上游系统自己的协议。这时可以使用Phoenix的Subscribe功能,扩展订阅的功能,做协议转换,分发,广播等操作。

如上图所示,Subscribe是用户自定声明注入到Phoenix框架的(Phoenix目前提供默认的KafkaSubscribe),其功能如下:
- Subscribe可以控制Phoenix接收消息的并发粒度,以KafkaSubscribe为例,每个Partition则会生成一个ReceiverActor来复杂消息拉取。
- Subscribe提供SourceCollect接口,当框架拉下数据之后,会调用SourceCollect接口进行数据的反序列化以及转换操作(后面会讲解该接口)。
有了Subscribe,用户即可灵活的订阅各种Topic,并��且自己完成协议的转换(上游协议转聚合根的命令),以及广播等操作。
Subscribe使用
用户不需要自己编写Subscribe,可以直接使用Phoenix提供的KafkaSubscribe(将来也会支持更多的消息队列),使用时只需要构造该对象,启动时给到Phoenix即。
在phoenix-spring-boot-starter中,可以直接把KafkaSubscribe丢给Spring容器即可。
@Configuration
public class PhoenixSubscribeConfig {
@Bean("customSubscribe")
public Subscribe customSubscribe() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.putIfAbsent(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_OFFSET_RESET_CONFIG, "latest");
return new KafkaSubscribe(
mqAddress, subscribeTopic, appName, properties, new SourceCollect());
}
}
KafkaSubscribe可以通过自定义Properties来设置Topic消费的额外配置,Properties是Map类型,Key和Value都是String类型,并且Key是ConsumerConfig类中的常量值,Value对应Kafka相关配置。
可以注意到,除了Kafka基本的配置之外,用户还需要提供一个SourceCollect的实现。
KafkaSubscribe 默认会订阅 Topic 下的所有 Partition, 但是用户也可以通过以下方式自定义订阅 Partition
@Configuration
public class CustomPartitionSubscribeConfig {
@Bean("customPartitionSubscribe")
public Subscribe customPartitionSubscribe() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.putIfAbsent(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_OFFSET_RESET_CONFIG, "latest");
return new KafkaPartitionSubscribe(
mqAddress, subscribeTopic, appName, properties, new SourceCollect());
}
/**
* 继承的 KafkaSubscribe 实现,重写 split()
*/
class KafkaPartitionSubscribe extends KafkaSubscribe {
public KafkaPartitionSubscribe(String mqAddress, String topic, String group,
Properties properties, SourceCollect sourceCollect) {
super(mqAddress, topic, group, properties, sourceCollect);
}
@Override
public List<SplitId> split() {
// 修改分片ID, 只返回一个 PartitionID = 0.
// 父类中则是通过 KafkaProducer 获取全部 PartitionNum, 然后生成同数量的 SplitID
return Arrays.asList(new SplitId(super.getSplitRangeId(), 0));
}
}
}
SourceCollect使用
SourceCollect是消息转换器,当Phoenix从上游拉取到消息之后,会调用SourceCollect来实现数据反序列化和数据转换操作。
用户可以自定义实现SourceCollect接口来实现上游数据到本集群命令的转换。如下案例所示:
- 根据records.getKey()获取上游放入的className。
- 如果匹配事件一致则进行反序列化(这里模拟了事件是JSON序列化的,实际应用当中应根据上游发送的协议进行反序列化)
- 根据上游事件内容构造本业务系统聚合根可以处理的命令并返回。
public class SelfSourceCollect implements SourceCollect {
@Override
public List<CollectResult> collect(Records records, CollectMetaData collectMetaData) {
List<CollectResult> collectResults = new ArrayList<>();
if (UpperAccountAllocateEvent.class.getName().equals(records.getKey())) {
// 反序列化上游事件
UpperAccountAllocateEvent upperAccountAllocateEvent = JsonUtil.decode(new String(records.getValue()), records.getKey());
// 根据上游事件要素构造出聚合根的cmd
Account.AccountAllocateCmd accountAllocateCmd =
Account.AccountAllocateCmd.newBuilder()
.setAccountCode(upperAccountAllocateEvent.getaccountCode())
.setAmt(upperAccountAllocateEvent.getAmt())
.setAllocateNumber(UUIDUtils.genUUID())
.build();
collectResults.add(new CollectResult(accountAllocateCmd, true));
}
return collectResults;
}
}
可以看到,Collect的返回体是List,如果上游事件内要素可以做到构造出多个不同聚合根的命令(聚合根id)不同,则可以返回多个命令,来让多个聚合根实例处理。
广播
功能介绍
通过上面订阅模型的介绍,我们知道SourceCollect在转换一个上游事件时可以返回多个命令来让多个聚合根处理,前提是需要能在上游事件中提取出能符合发给多个聚合根对象的属性。
有时上游事件无法完整的构造出本业务的聚合根可以处理命令(上游事件当中没有构造聚合根id所需要的要素),但却有相关要素。比如,一个基金产品聚合根有用很多股票持仓,当某只股票价格变化(上游事件),希望触发所有有这只股票的产品聚合根重新计算资产。
我们可以在产品聚合根处理持仓(新增和删除持仓)时,向ReceiverActor注册一个元数据(产品001 -> 股票001)。在ReceiverActor拉取到股票的变更事件后,便会在调用SourceCollect#collect把该元数据传递给用户定义的实现类,
这样用户就可以方便的拿到哪些产品拥有该只股票,进而构造出行情变更命令,触发重新计算净资产。
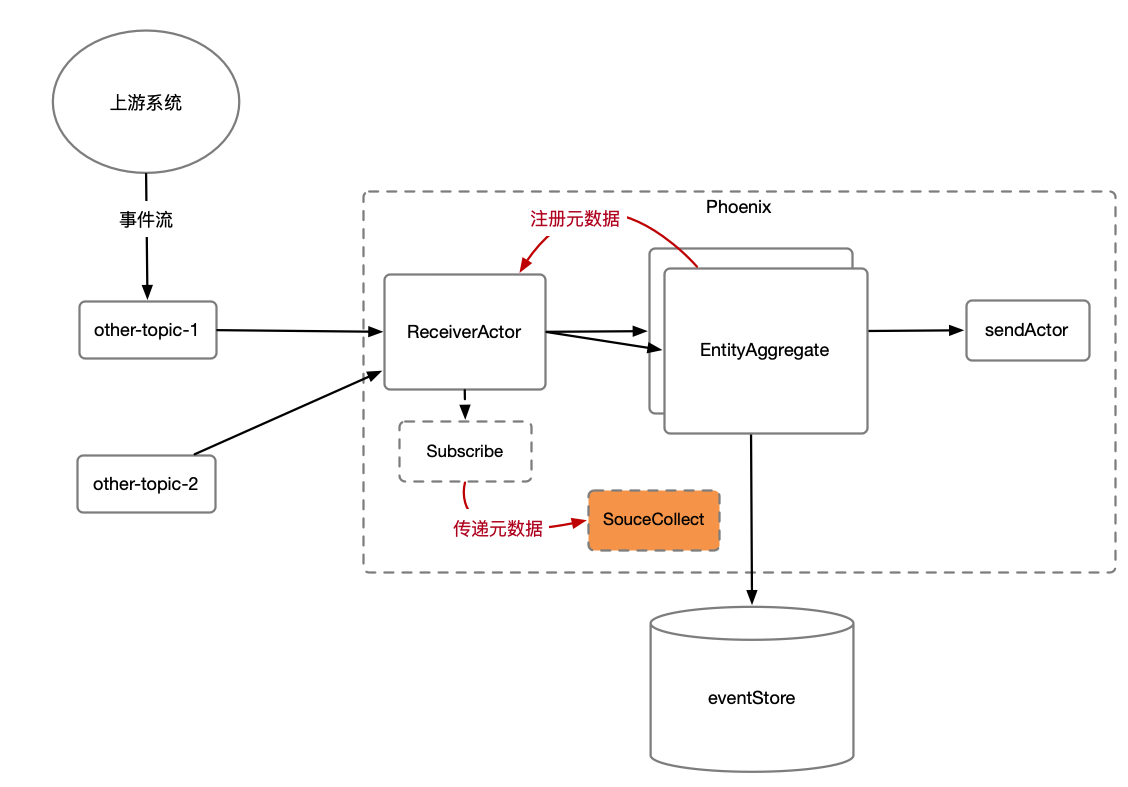
如上图所示,Phoenix可以保证该元数据(CollectMetaData)可以最终一致的可靠存储下来,Phoenix提供方便的注册元数据以及取消注册元数据的功能。
注册CollectMetaData
在实体聚合根的Command处理方法中,用户可以自定义注册CollectData到Topic的处理端(SourceCollect)。
@CommandHandler(aggregateRootId = "fundCode", isCommandSourcing = true)
public ActReturn act(PositionChangeCmd positionChangeCmd) {
// 处理持仓变更的业务逻辑
// dosomething...
RegistryCollectData registryCollectData = null;
// 新增持仓时注册元数据
if(positionChangeCmd.type == ADD) {
registryCollectData = new RegistryCollectData(RegistryCollectData.Type.REGISTRY,
KafkaSubscribe.genSplitRangeId(mqAddress, subscribeTopic),
Arrays.asList(positionChangeCmd.getSecuCode())
fundCode);
}
// 删除持仓时删除元数据
// .. 构造 RegistryCollectData.Type = UN_REGISTRY
// 返回
retrun ActReturn.builder()
.registryCollectData(registryCollectData)
.其他要素
.build();
}
注意:在用户配置了聚合根的存活时间后,当实体聚合根从内存中淘汰后,框架会自动取消该聚合根所有的注册数据,并且在聚合根恢复后,也不会自动恢复注册。
@EntityAggregateAnnotation(
aggregateRootType = "BankAccountAggregateBroadCast",
surviveTime = 1000 * 60 * 10) // 10分钟后淘汰聚合根,自动取消所有注册
使用CollectMetaData
上面产品聚合根向ReceiverActor注册了元数据(CollectMetaData),这样用户在编写SourceCollect时则可以获取元数据,转化命令。
public class MarketEventCollect implements SourceCollect {
@Override
public List<CollectResult> collect(Records records, CollectMetaData collectMetaData) {
List<CollectResult> collectResults = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// 反序列化股票行情变更事件
MarketEvent marketEvent = JSON.enCode(records.getKey, records.getValue());
// 获取注册的元数据: 哪些产品聚合根拥有该只股票持仓
Set<String> metaDataValue = collectMetaData.getMetaDataValue(marketEvent.getSecucode());
for (String fundCode : metaDataValue) {
// 构造产品聚合根的行情变更命令
MarketChangeCmd marketChangeCmd = new MarketChangeCmd(fundCode, marketEvent);
collectResults.add(new CollectResult(marketChangeCmd, true));
}
} catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return collectResults;
}
}
可以看到,通过实体聚合根注册元数据,和SourceCollect转换时获取该笔元数据转换,进而完成了行情驱动资产变更的模型。实际上,用户可以根据业务需求,灵活的给自己的产品聚合根打标签,来完成更复杂精确的消息转换任务。